Monday April 29 th
11:15am - 11:30am
Location: East 2/3
Presentation Number: 1702
Author:
Baruch D. Kuppermann 1
, Ian Parrag 2
, Dimitra Louka 2
, Hans Fischer 2
, Gillian Mackey 2
, Ben B. Muirhead 3
, Emily Anne Hicks 3
, Heather Sheardown 3
, Wendy Naimark 2
1
Gavin Herbert Eye Inst. UCI Dept Ophthal, University of California Irvine, Irvine, California, United States;
2
Interface Biologics, Toronto, Ontario, Canada;
3
Biomedical Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada;
Purpose
Local drug delivery via surface erosion enables highly controlled, sustained release of drug. We have developed a novel approach to drug delivery in the eye that employs an erosion-based mechanism of drug release from a fully degradable, nonpolymeric implant. The lead product in development is an intravitreal implant (IBE-814 IVT) that releases dexamethasone to treat posterior inflammatory conditions. We have evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of the IBE-814 IVT implants in rabbits to demonstrate sustained dexamethasone release for ~6 months with implants delivered through a 30G needle.
Methods
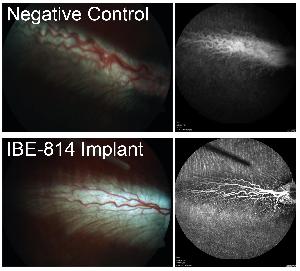
PK of the IBE-814 IVT implants were tested in New Zealand white rabbits following intravitreal injection of the implants. Terminal time points of 1, 2, 8, 16, 26, and 40 weeks were used and drug was quantified in ocular tissues by LC/MS/MS. A rabbit VEGF-induced vascular leakage model was used to test the PD of IBE-814 IVT implants in inhibiting blood-retinal barrier breakdown. Dutch Belted rabbits underwent bilateral intravitreal injection on Day 0 and vascular leakage was induced by VEGF (1000 ng/eye) at 1, 10, and 26 weeks post-implantation. Inhibition of VEGF-induced vascular leakage was evaluated by fundus microscopy and fluorescein angiography. Commercially available dexamethasone implants were used as a control in both studies.
Results
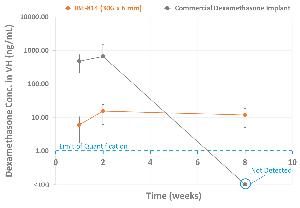
The IBE-814 IVT implants released a low and consistent dose of dexamethasone (~6-15 ng/ml) in the vitreous humour of the rabbit eye out to at least 8 weeks, with later time points ongoing. In contrast, commercial dexamethasone implants had an initial burst release with no drug detected in the vitreous humor at week 8. The low, consistent dose of dexamethasone released from the IBE-814 IVT implants inhibited VEGF-induced vascular leakage at weeks 1 and 10 in the VEGF model as observed by fluorescein angiography. Commercial dexamethasone implants inhibited VEGF-induced vascular leakage at week 1 but not at week 10.
Conclusions
The IBE-814 IVT implant is a novel biodegradable surface-eroding implant delivered with a 30G needle that releases a low, consistent, and efficacious dose of dexamethasone out to at least 10 weeks in rabbits. Ongoing studies will assess drug release out to ~6 months.
Layman Abstract: Provide a 50-200 word description of your work that non-scientists can understand. Describe the big picture and the implications of your findings, not the study itself and the associated details.
The IBE-814 IVT implant is a fully degradable, non-polymeric intravitreal implant designed to deliver a consistent, low dose of dexamethasone for posterior ocular inflammatory diseases. The target implant will be injected with a minimally invasive 30 gauge needle and will be able to deliver a low dose of dexamethasone for approximately 6 months. The development of an effective low-dose, 6-month steroid-releasing invtravitreal implant has the potential to decrease repeat treatment frequency.